Which Best Describes the Tertiary Structure of a Protein
Hemoglobin is a globular protein composed of a single polypeptide chain that has one O 2 binding site. 07 Which of the following descriptions best describes the primary structure of proteins.

1 The Four Levels Of Protein Structure The Primary Structure Download Scientific Diagram
How many types of amino acids.
. Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein Answers. Which best describes protein tertiary structure A The sequence of amino acids B. In which case would a scientist choose to use a dissecting microscope rather than a compound microscope.
After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. If this structure is disrupted or disturbed a protein is said to be denatured which means it is chemically affected and its structure is distorted. The R group is one of the four parts of the amino acid structure which is different for all amino acids.
Several polypeptides held together by ionic polar or covalent bonds. 3D globular structures stabilized by covalent disulfide bridges is the tertiary structure of a protein molecule. According to this question the tertiary structure of the protein is formed as a result of the interaction of different R groups with one another and their environment.
Orders of protein structure. The tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Primary structure refers to the order of the amino acids in a protein.
Which of the following best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. To some extent the tertiary structure is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure. Which of the following best describes where these two amino acids are most likely to be found in the tertiary structure of a protein based on the residuest HON EN HUN in the hydrophilic Interior of the protein due to their ability to form side chain hydrogen bonds with each other in the interior of the folded protein away from water due to their hydrophobic.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. A protein has been made from the.
These structures are stabilised by the several types of bonds namely hydrogen bond ionic bond van der waals interaction covalent bond disulphide bridges and. It is allowed to grow and change as more is learned about the product and its customersB. The polypeptide chain may undergo coiling and folding to produce the tertiary structure.
The tertiary structure consists of eight beta-strands connected by α-helices known as the globin fold Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of two different types of globin subunits each of which has an O 2 binding site. Proteins structures are made by condensation of amino acids forming peptide bonds. Step-by-step explanation The primary structure of a protein is the linear chain of the amino acids that are joined by peptide bond.
Biology questions and answers. 2 Get Other questions on the subject. Tertiary Structure refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a proteinThere are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure.
A single polypeptide chain folded into a three-dimensional shape by ionic polar or covalent bonds. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. Biology 21062019 2130 nnamdi.
Which of the following describes the tertiary structure of proteins. The Tertiary Structure of a protein is the arrangement of the secondary structures into this final 3-dimensional shape. For instance in globular proteins the polypeptide chains are held together in a definite way forming a compact structure.
Which age group best describes you. The secondary structure is determined by the dihedral angles of the peptide bonds the tertiary structure by the folding of proteins chains in space. The sequence of amino acids in a protein the primary structure will determine where alpha helices and beta sheets the secondary structures will occure.
The tertiary structure is a single polypeptide chain that forms a globular shape bonded by hydrogen ionic disulfide and van der Waals bonds or hydrophobic interactions and the interaction between R-groups. Specific biological activities such as enzyme activity are associated with the tertiary structure. Permanent loss of protein structure.
A-Characteristic patterns such as helices and sheets that arise when hydrogen bonds form between the amino acids of polypeptides b-The association of multiple polypeptides c-The linear sequence of amino acids making up the polypeptide d-Interactions between different. The association of separate subunits into a multip CAlpha beliciei and beta sheets D Folding of the polypeptide chain 0 that amino different kind. The tertiary structure is maintained by many.
The tertiary structure of the protein is determined by the interactions of the different R-groups with other R-groups and with their environment in the protein Option B. The secondary structure is a helix or pleated sheet mad eof hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups. This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins.
Tertiary structure of a protein describes A The order of amino acids B Location of disulphide bonds C Loop regions of proteins D The ways of protein folding. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a proteinThe R group of the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Complete set of proteins.
A linear chain of amino acids held together by covalent bonds. Secondary structure indicates regions of ordered structure and tertiary structure is. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure.
At this level every protein has a specific three-dimensional shape and presents functional groups on its outer surface allowing it to interact with other molecules and giving it its unique function. The amino acid sequences is controlled by the nucleotide codons of mRNA. The arrangement is made with the help of chaperones which move the protein.

Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Youtube

Protein Tertiary Structure Showing Pore Morphology Of Gmtip1 5 And Download Scientific Diagram

A Primer For Protein Structure Walk In The Forest

Free Protein Structure Biochemistry Homework Page Science Teaching Resources Biology Classroom Biology Lessons
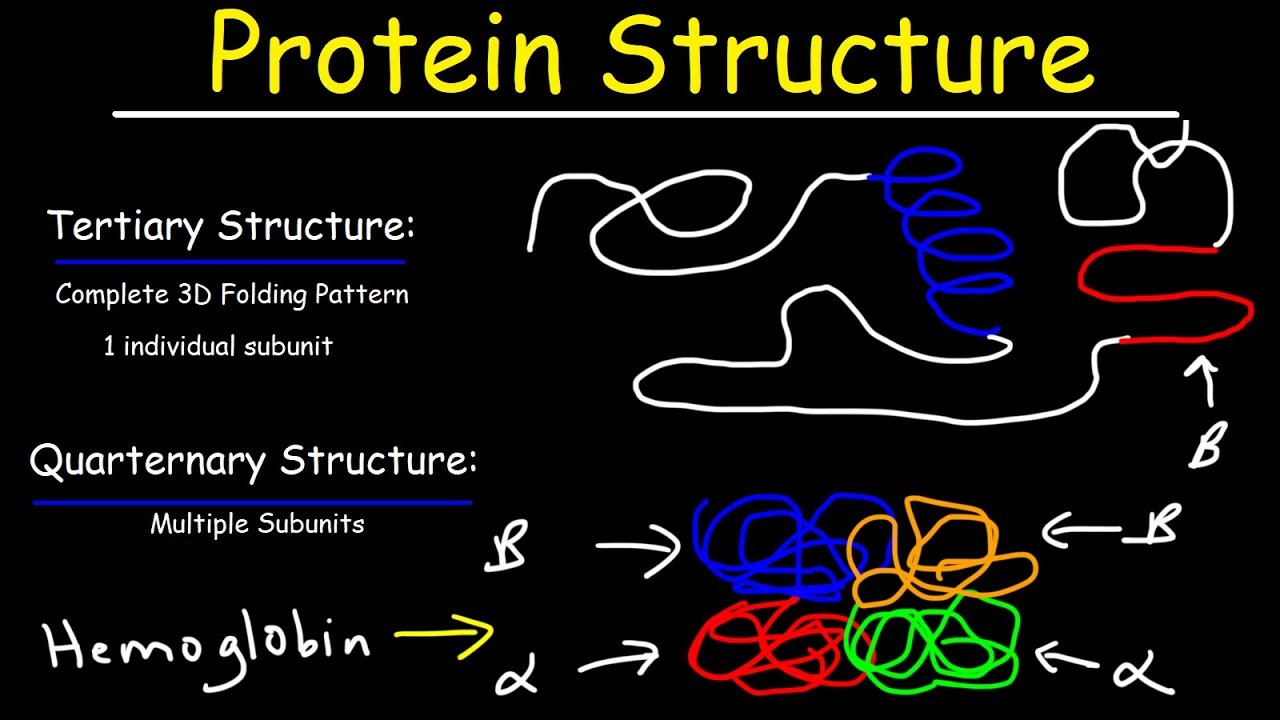
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Biology Youtube
How Does The Structure Of Protein Relate To Its Function Quora

The Hierarchical Structure Of Proteins The Primary Structure Is Download Scientific Diagram
How Is The Tertiary Structure Of Protein Formed Quora

Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quatrenary Article Khan Academy Protein Biology Biology Macromolecules
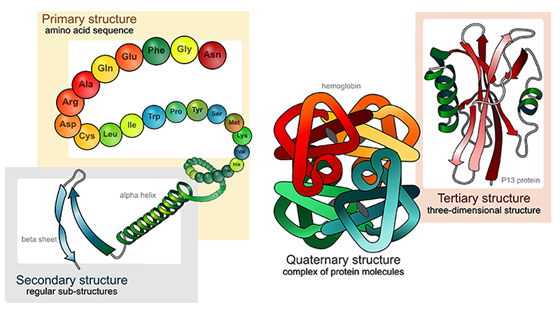
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures
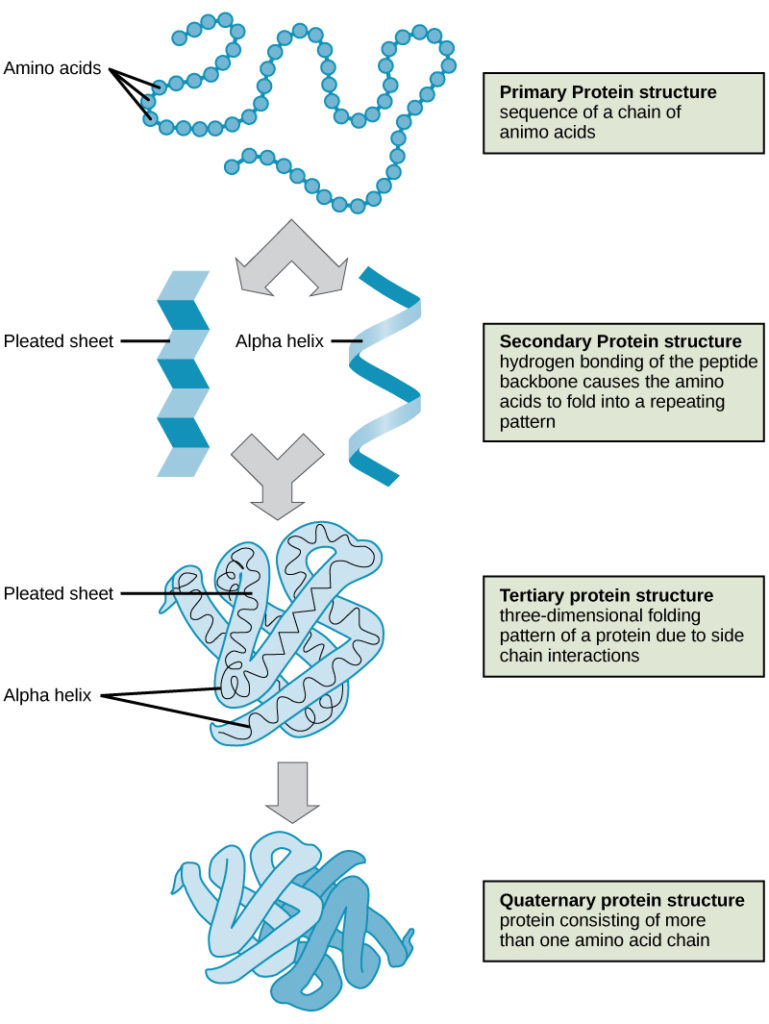
Protein Structure Biology For Non Majors I

Microbiology Bring It On Map Screenshot

The Thermodynamics Of Protein Folding Depicted As A Free Energy Funnel Biology Forums Gallery Protein Folding Free Energy Thermodynamics
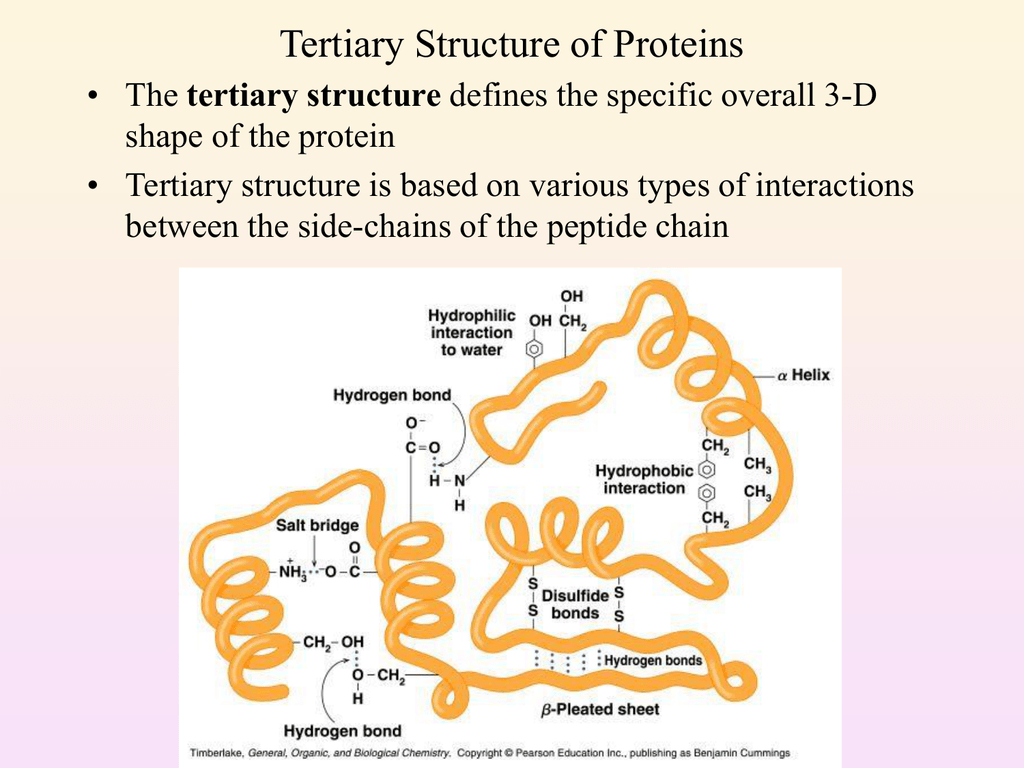
Tertiary Structure Of Proteins

Primary Secondary Tertiary And Quaternary Structures Of Proteins Youtube

How Are Protein Molecules Structured Quora

David Chalk Teacherchalky1 Twitter Middle School Science Activities Teaching Biology Medical Student Study

Tertiary Structure Protein Structure Tutorials Msoe Center For Biomolecular Modeling
